Top Tool Steel Factory
FCS Tool Steel
High Quality Cold/Hot/Plastic/High-speed Tool Steels
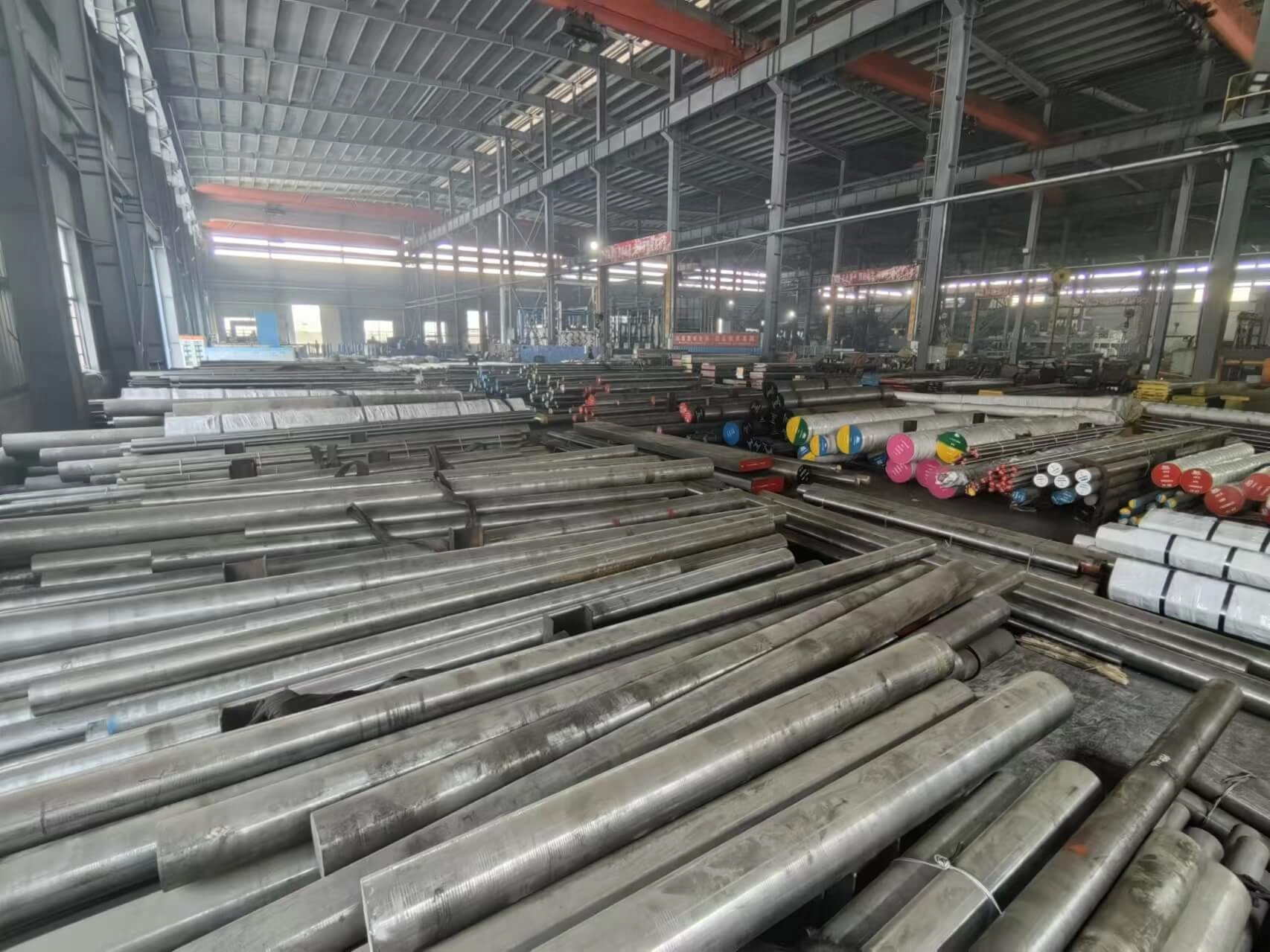
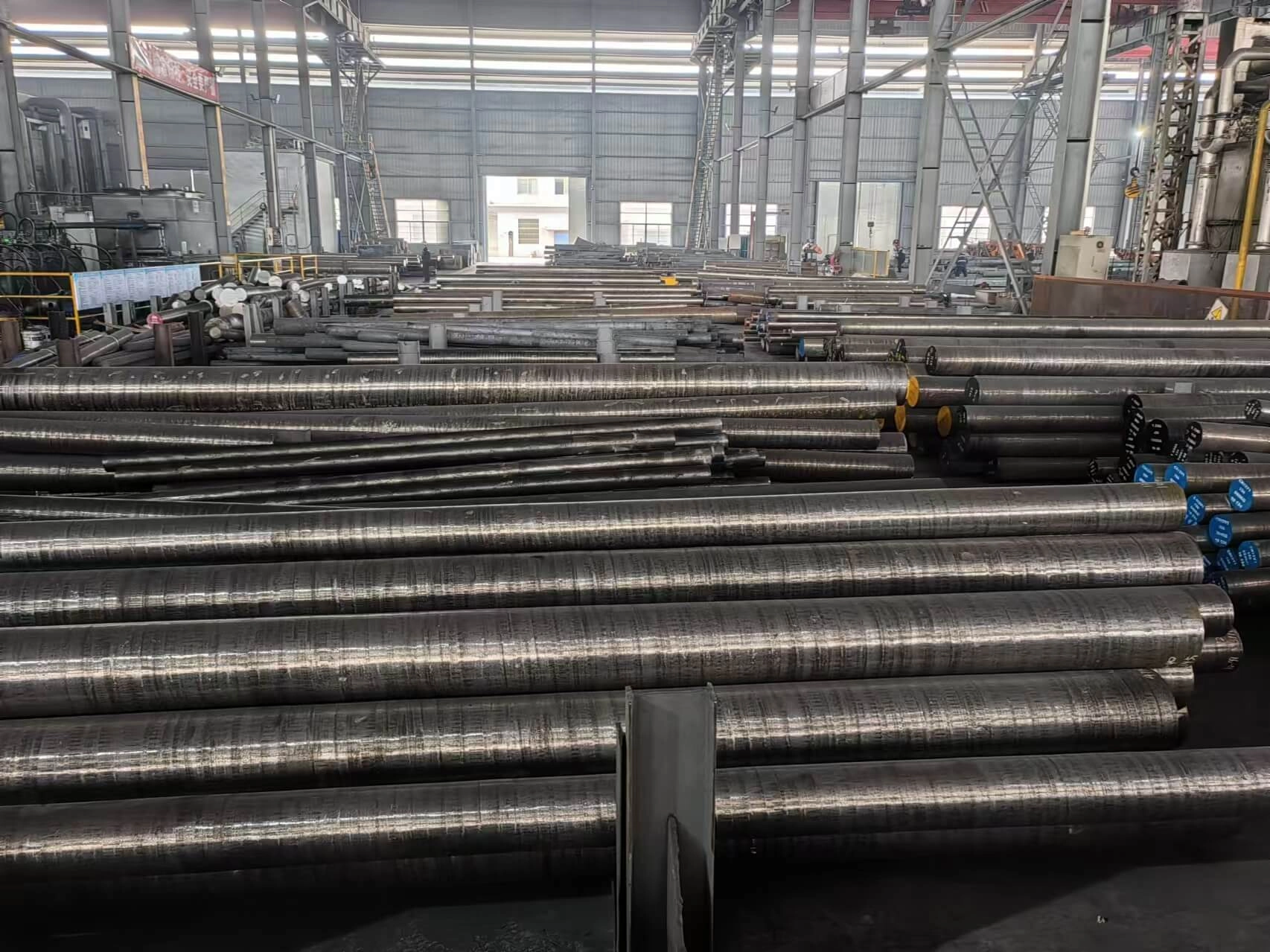
Big Tool Steel Workshop Warehouse
The workshop covers an area of 40,000 square meters, and the warehouse has a long-term stock of 2,000 tons of tool steel. We have a wide range of tool steels, cold work tool steel, hot work tool steel, plastic tool steel, high speed tool steel and stainless steel. Tool steel customization services are also available.


Tool steel production equipment
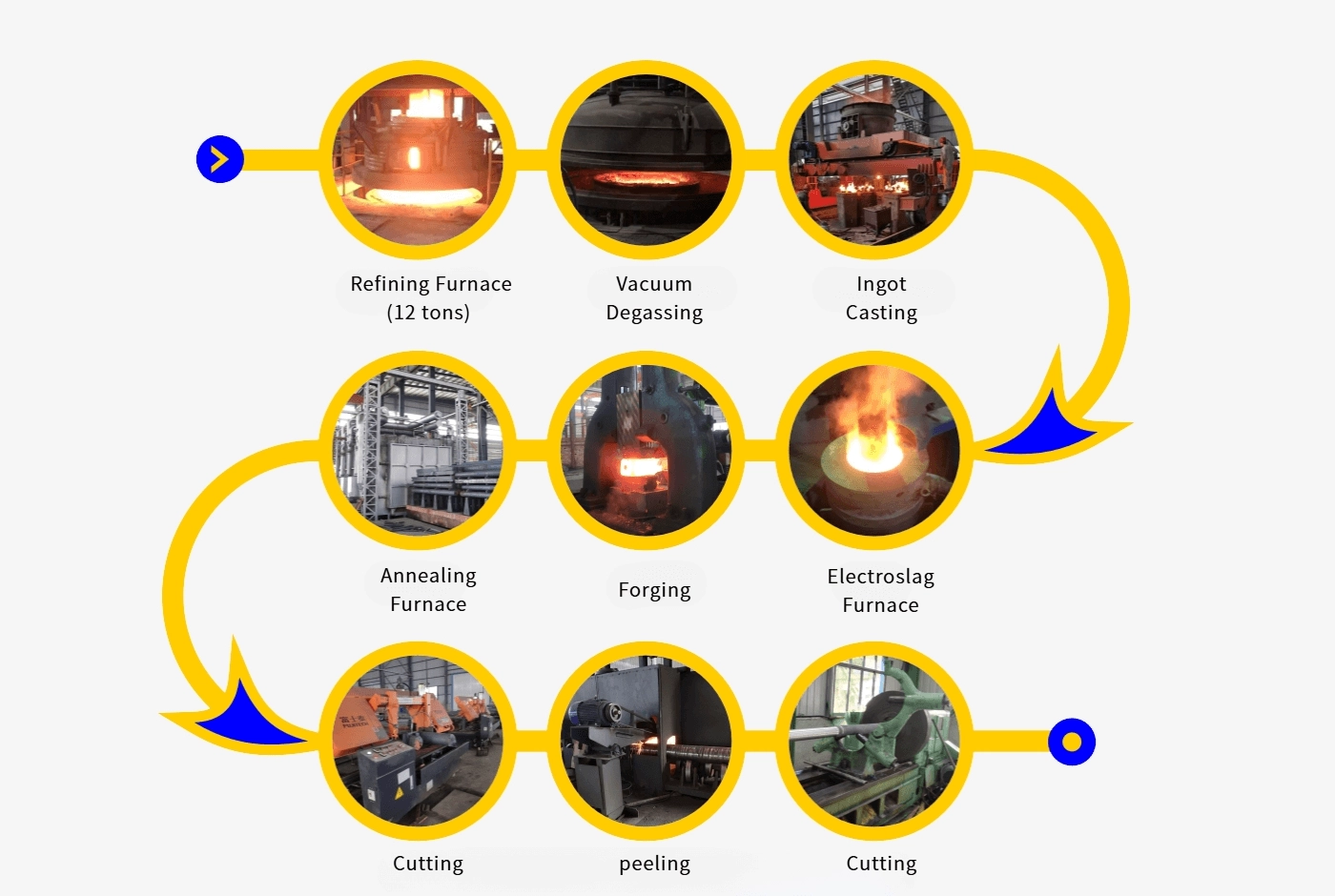
Our main equipment includes 10 tons of electric hydraulic hammer, 10 tons of off-furnace refining equipment, vacuum degassing equipment and multiple electroslag remelting furnaces to ensure the high quality and technical content of products.
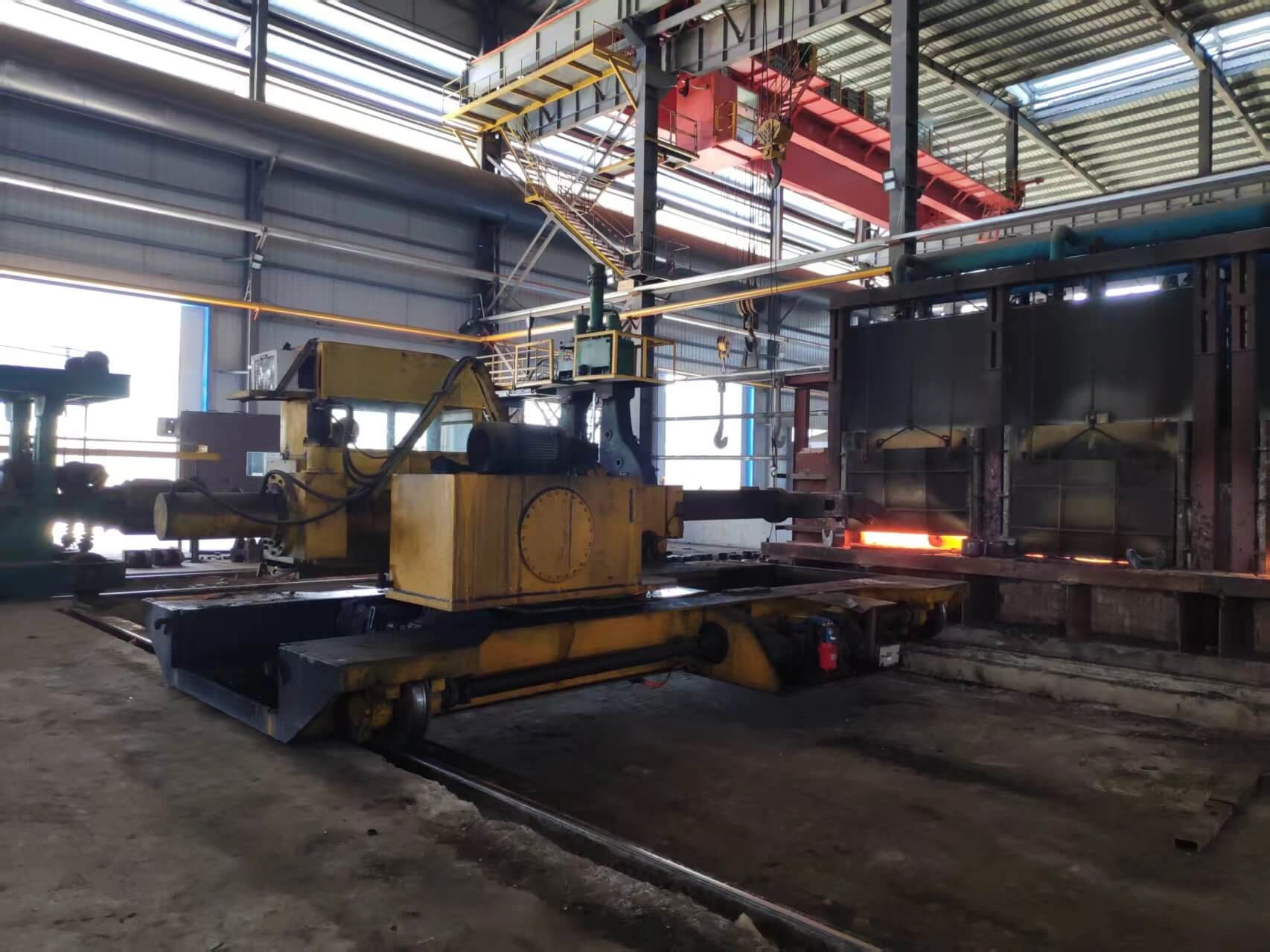
Charging Machine
A charging machine is a critical industrial device used to load raw materials (e.g., scrap metal, alloys) into furnaces or reactors during tool steel production.It ensures efficient, automated, and precise material handling, reducing manual labor and enhancing process consistency. Integrated with PLC systems, these machines optimize temperature control and material distribution, crucial for maintaining alloy composition and furnace efficiency in tool steel manufacturing. Features like argon injection for stirring molten steel (from ladle furnace practices) may also complement charging operations to ensure uniformity. Their automation reduces oxidation risks and improves safety in high-temperature environments.
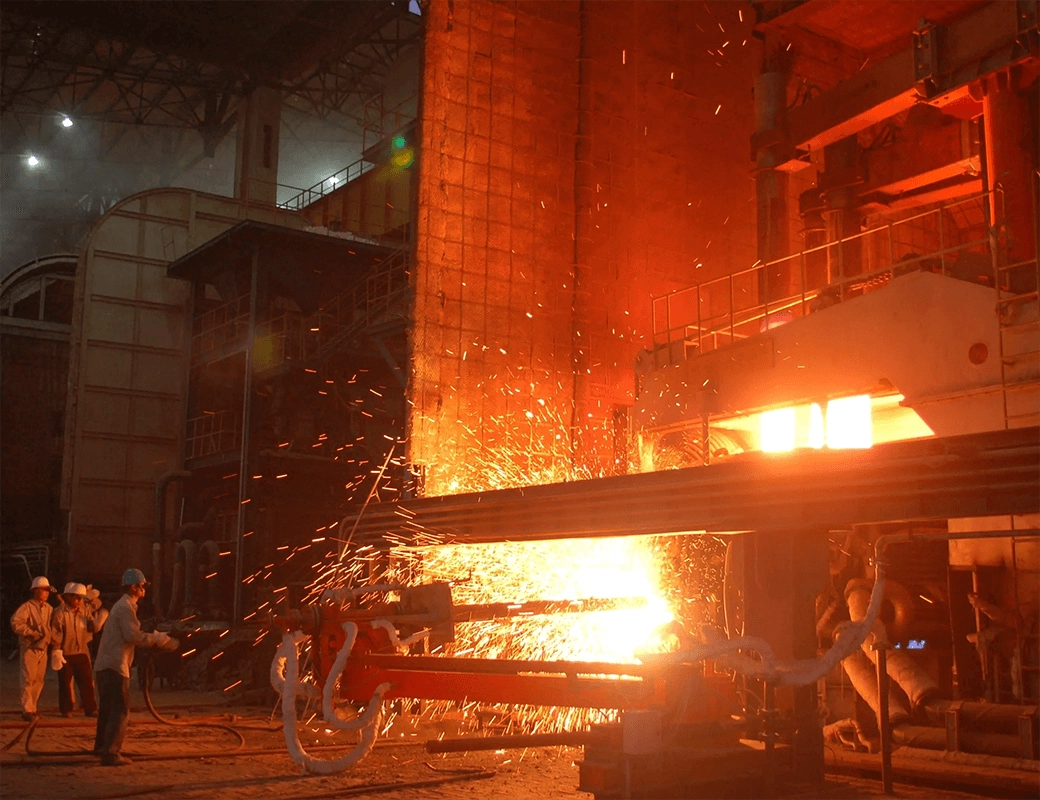


Electic Furnace(EF)
Electroslag Remelting (ESR)
.webp)
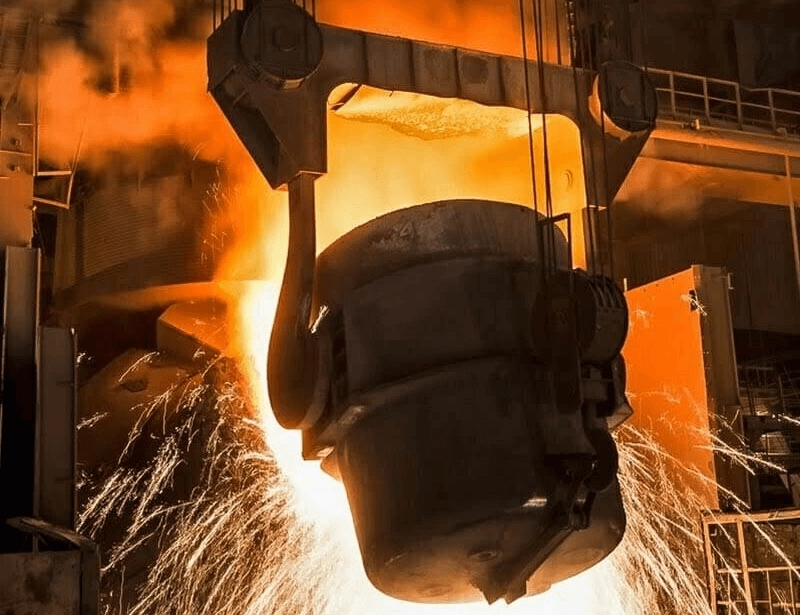

Ladle Furnace (LF)
Ingot Casting
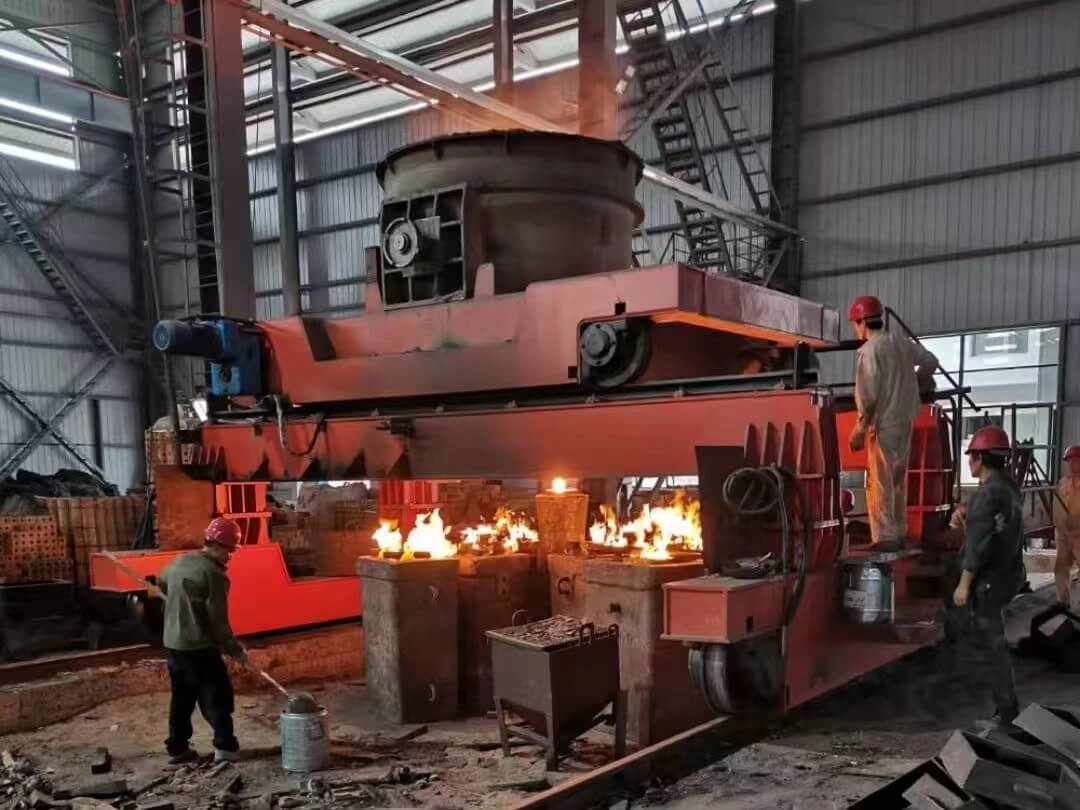
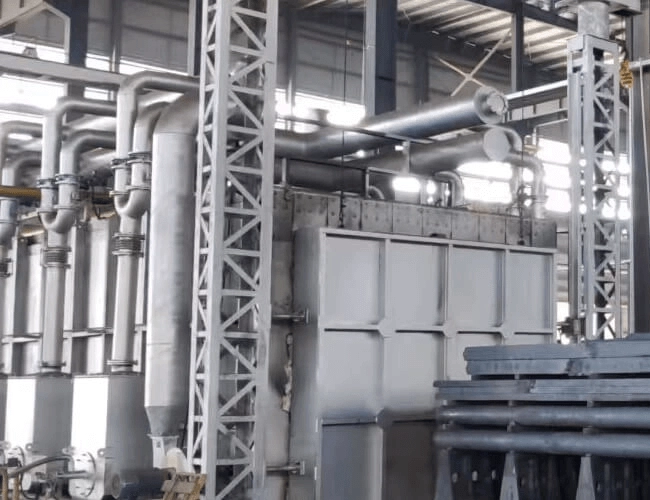


Annealing Furnace
Sawing Machine
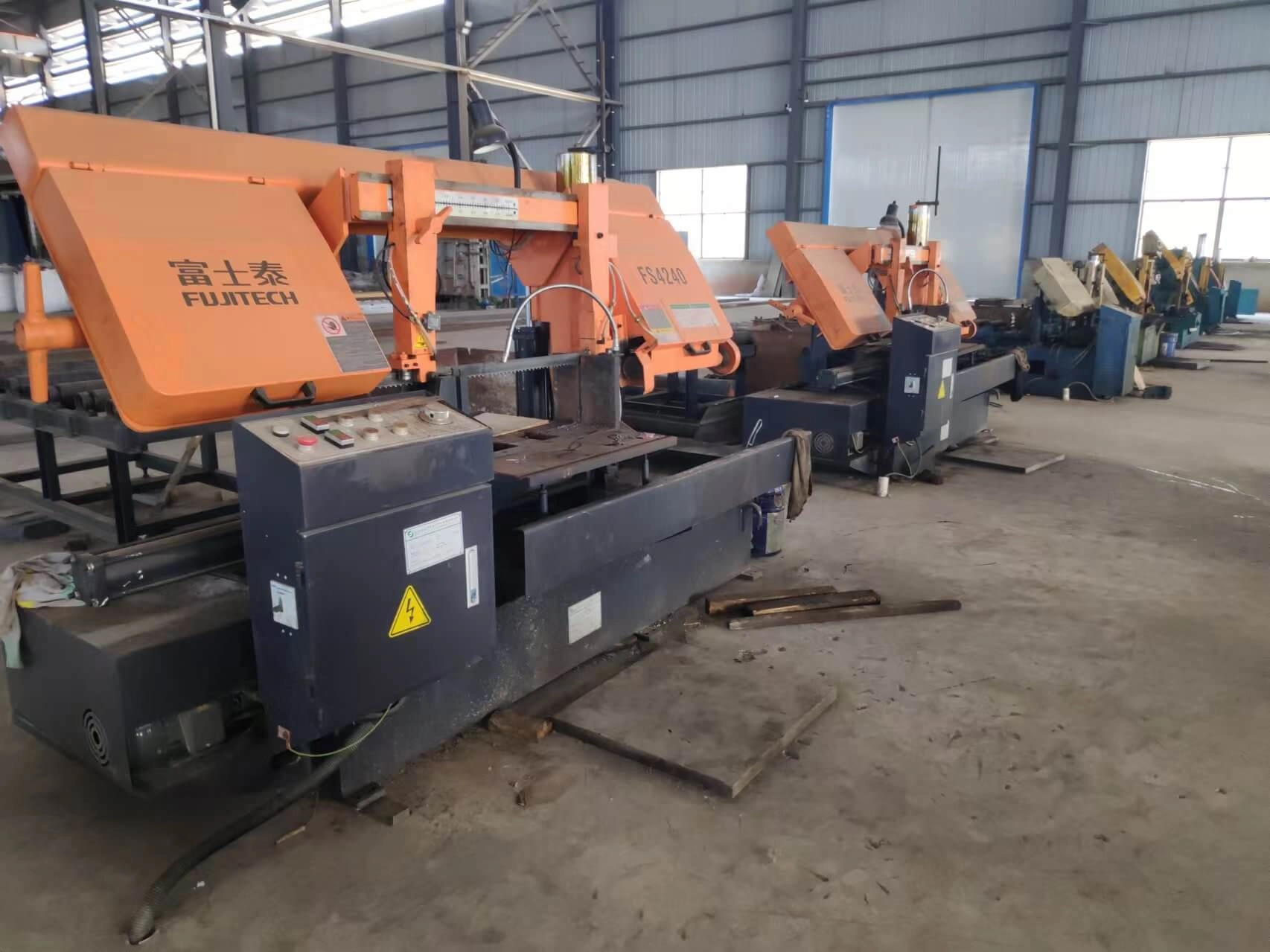
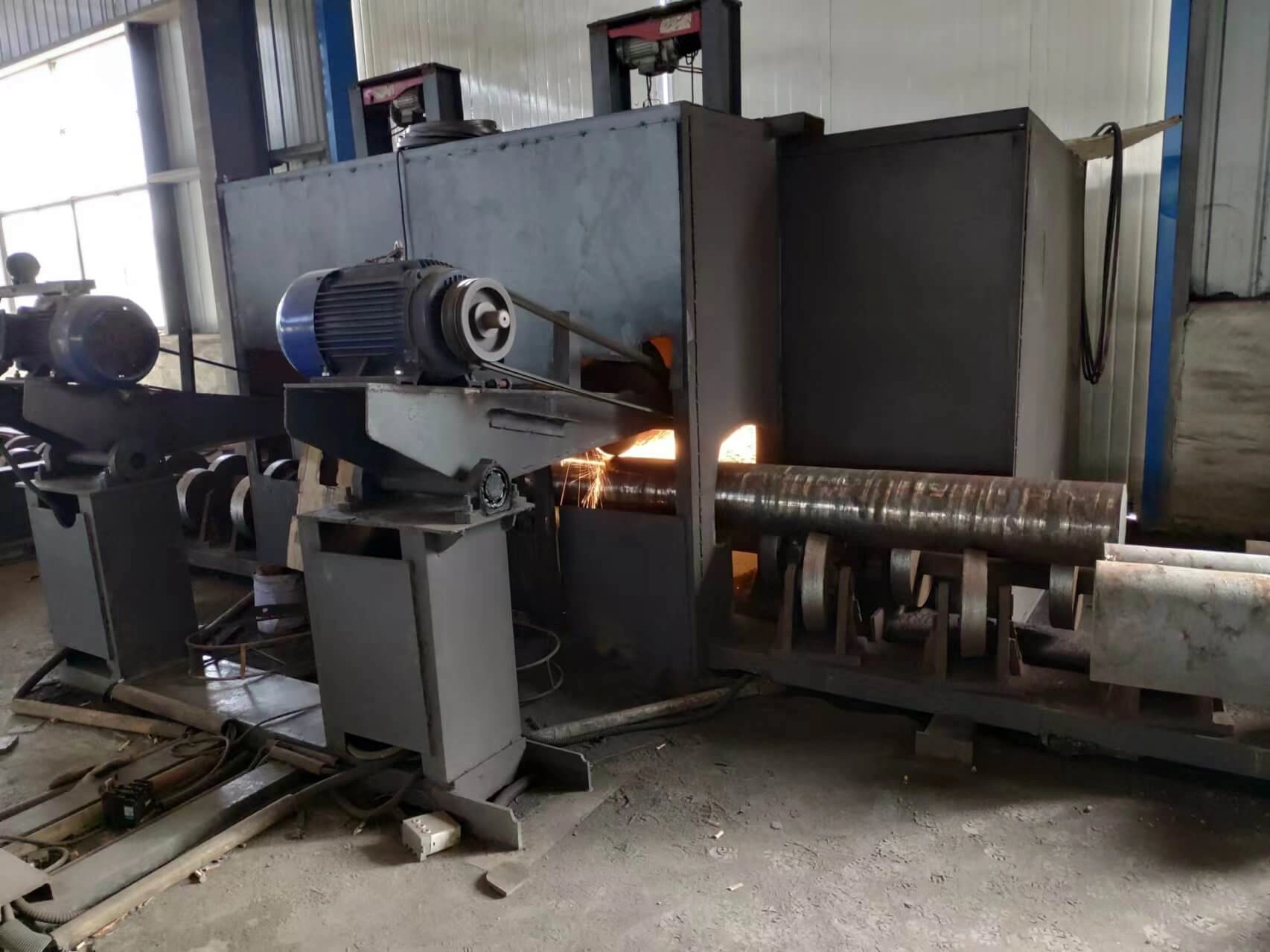


Peeling Machine
A peeling machine for tool steel is a specialized piece of equipment used in the manufacturing process to remove material from the surface of tool steel bars or rods. The primary purpose is to achieve precise dimensions and improve surface quality. The peeling process typically involves rotating the steel workpiece against a cutting tool, which shaves off a thin layer of material, resulting in a smooth, uniform finish.
Turning/Milling Machined
Turning and milling are machining processes used to shape tool steel into precise geometries required for various applications. Turning involves rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, typically performed on a lathe, to create cylindrical shapes, while milling involves cutting the workpiece with a rotating tool to produce complex surfaces, slots, and contours, typically performed on a milling machine. Both processes require careful selection of cutting tools and parameters to manage tool wear, achieve desired surface finishes, and maintain dimensional accuracy, making them essential for manufacturing high-quality tool steel components used in tooling and machinery.
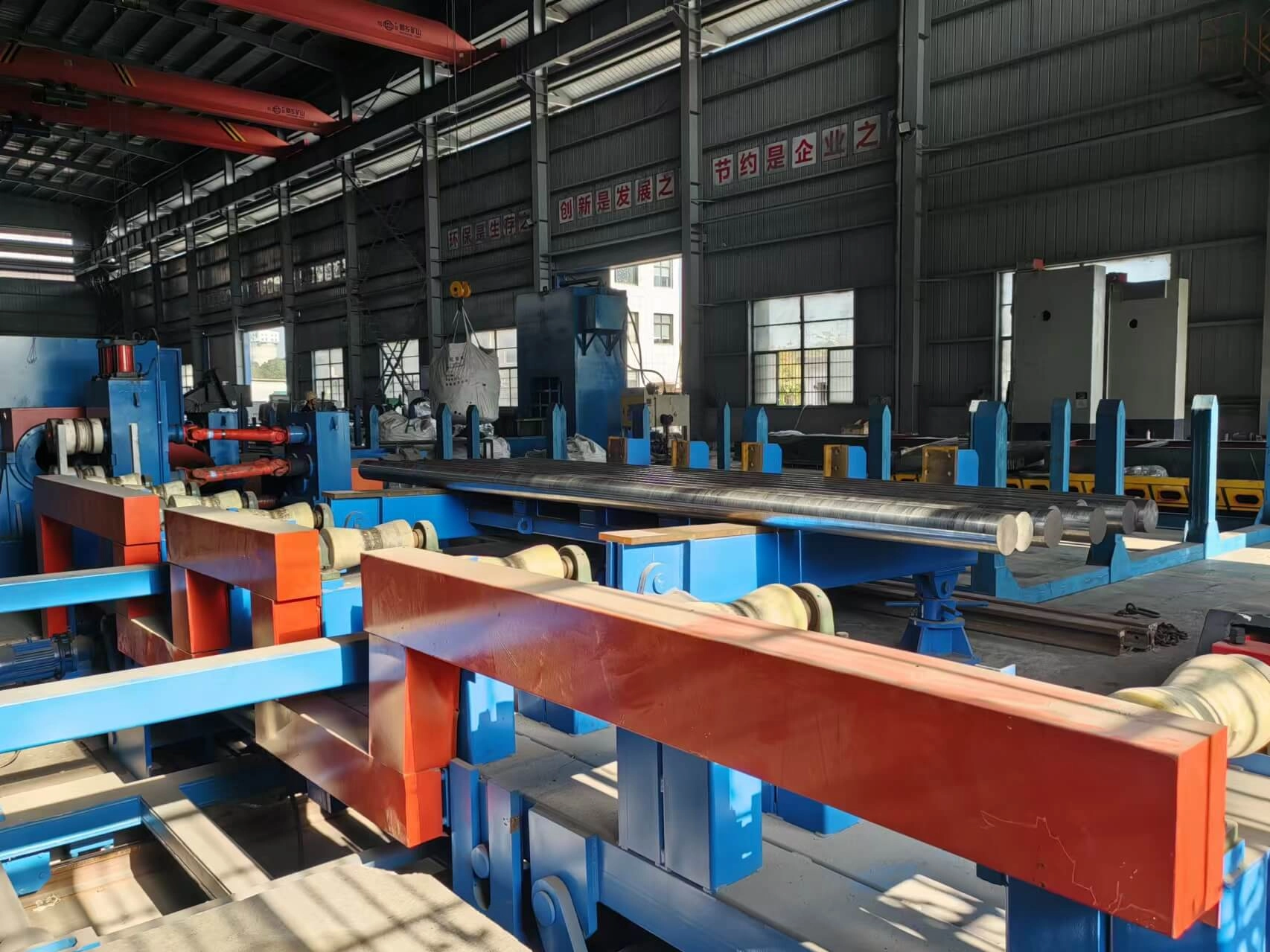

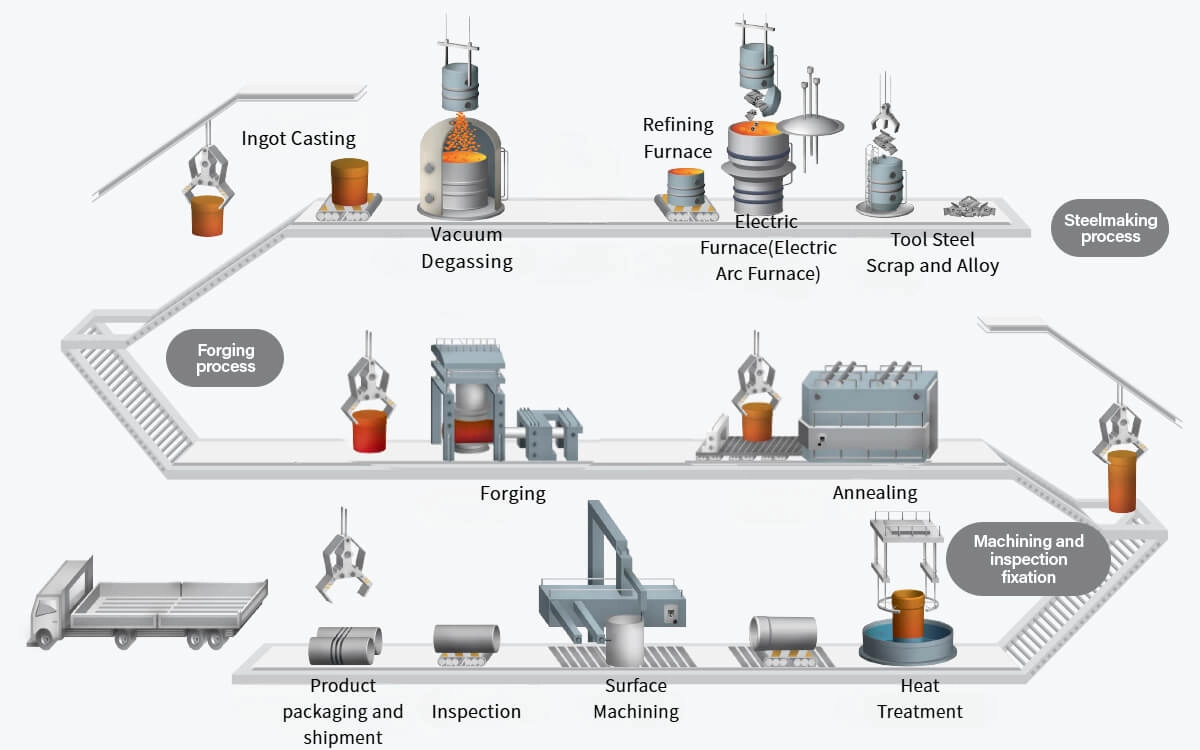
Tool steel Manufacturing
The workshop covers an area of 40,000 square meters, and the warehouse has a long-term stock of 2,000 tons of tool steel. We have a wide range of tool steels, cold work tool steel, hot work tool steel, plastic tool steel, high speed tool steel and stainless steel. Tool steel customization services are also available.
Material Remelting
First, tool steel scrap and alloy materials are gathered for recycling and composition. These materials are then melted in an electric furnace to achieve a molten state before being transferred to a refining furnace for further purification. This process includes vacuum degassing to remove any dissolved gases, which significantly enhances the steel quality.
Ingot Casting & Forging
Processing & Heat Treatment
After cooling, the material is machined and subjected to inspection fixation for precise dimensions. To enhance mechanical properties and harden the steel, heat treatment is applied, and a surface machine processes the steel to achieve a smooth finish.
Quality inspection