Choosing between 1.2343 tool steel and 1.2344 tool steels can greatly affect your project. They both work great.But they excel in different areas like heat resistance, wear, or machinability. Are you unsure which steel to use for your next heavy-duty job? One of these could be just what you need. However, there’s one important factor to consider that might change your decision.
Chemical Composition
Tool steels’ composition works like a secret formula. This formula decides how well they perform and what jobs they handle best. Take grades 1.2343 and 1.2344. Their carbon, vanadium, and other element ratios create the right balance for specific tasks. I find it’s like selecting the proper tool. Each grade has unique strengths and features made for particular challenges.1.2344 has much more vanadium (0.85-1.15%) than 1.2343 (0.30-0.50%). Vanadium boosts strength at high temperatures. It also improves wear resistance and hot hardness.
Composition of 1.2343 (X37CrMoV5-1) and 1.2344 (X40CrMoV5-1)
| Steel Grade | Carbon (C) | Silicon (Si) | Manganese (Mn) | Chromium (Cr) | Molybdenum (Mo) | Vanadium (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2343 (X37CrMoV5-1) | 0.33-0.41% | 0.80-1.20% | 0.25-0.50% | 4.80-5.50% | 1.10-1.50% | 0.30-0.50% |
| 1.2344 (X40CrMoV5-1) | 0.37-0.45% | 0.80-1.20% | 0.25-0.50% | 4.80-5.50% | 1.20-1.50% | 0.85-1.15% |
How These Differences Matter
When it comes to tough tasks, 1.2344’s extra vanadium is like a shield, giving it incredible wear resistance. I’d definitely recommend it for the heavy-duty work where things are bound to get rough. It can take the heat—literally—thanks to the added vanadium and carbon, standing strong even under extreme conditions. On the other hand, 1.2343 has a bit less vanadium and carbon, which makes it tougher, like a reliable companion that bends without breaking. It’s perfect for jobs where you need that balance of flexibility and strength. So, if you’re facing high heat or wear-and-tear, go for 1.2344. But if toughness and flexibility are the stars of the show, 1.2343 has got you covered.
Properties and Performance
Comparing 1.2343 and 1.2344 tool steels shows clear differences in four areas: Toughness.Heat resistance .Hardness.Wear resistance. They’re like two strong competitors. Both last long, but each has strengths that decide success based on the job. I think small property changes strongly affect results in sudden heat situations or extended use. From my experience, it’s like picking between two good options. One handles heat slightly better. The other holds up against friction and abrasion over time.
Hardness
After heat treatment, both 1.2343 and 1.2344 tool steels become very hard. They reach 46 to 54 HRC. I’ve used both steels for tooling jobs, and they perform well in real-world situations.But let’s talk about heavy workloads. During high-speed cutting or molding tasks, I’ve noticed differences. 1.2343 handles sudden impacts better because it bends more easily. 1.2344 works differently—it keeps tools sharp longer and stays strong even when heated. This makes it better for jobs involving friction or heat.Need impact resistance? Pick 1.2343. Want something that lasts longer under friction? Choose 1.2344. Both steels deliver reliable results depending on your needs.
Toughness
The toughness of 1.2343 is better, which is suitable to withstand the alternating cold and hot conditions. 1.2344 pays more attention to the balance of strength and hardness.
| Tool Steel Grade | Elongation | Impact Toughness/Tensile Strength | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2343 | about 10 – 15% | 14 – 18 J/cm² | Has good plasticity and resistance to cold and heat fatigue |
| 1.2344 | Slightly lower (about 20%) | 1550 – 1850 MPa | Toughness is slightly less than 1.2343, but adjustable by tempering |
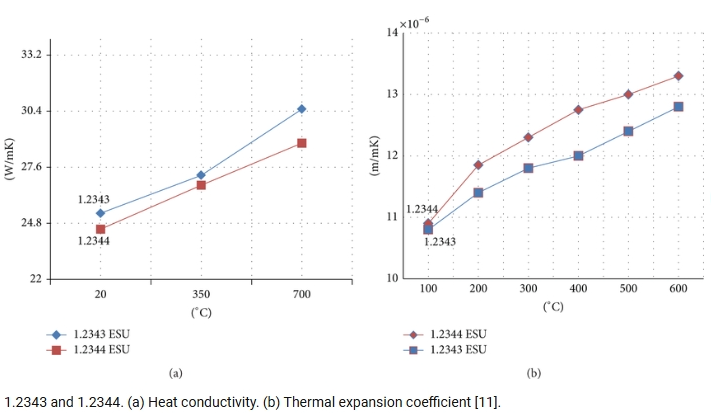
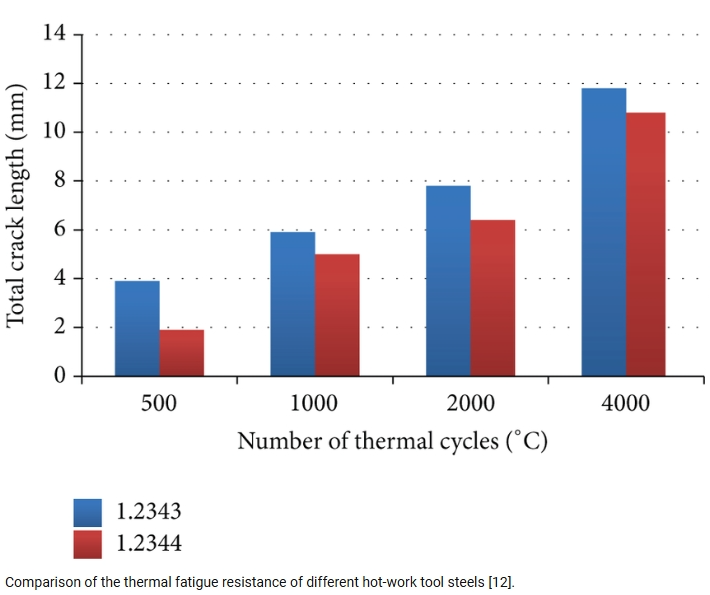
Heat Resistance
1.2343 tool steel has a wide range of heat-resistant temperatures. It is recommended to use a hardness of 40-50 HRC to maintain high temperature stability 1.2344 heat cracking performance is outstanding. High temperature strength is higher. Suitable for long-term work in 500-600℃ environment (such as aluminum die casting mold). Both are suitable for high temperature scenarios, but 1.2344 has better thermal cracking resistance and oxidation resistance at extreme high temperatures.
Service Life
In tough environments like die-casting, 1.2344 lasts longer than other materials. It can handle extreme heat and wear better than most. I saw this myself in a steel forging plant last year. The 1.2344 dies performed well under high temperatures, while others started to wear down. It keeps going even when conditions are tough. This durability in heat and friction is why it’s trusted for heavy-duty tasks, making it perfect for jobs that require both strength and precision.
Machinability
For shaping and cutting tool steels, 1.2343 machines better than 1.2344. I’ve worked with both grades and prefer 1.2343’s lower alloy content – it processes smoother for detailed tool shapes. Last month, we made a die-casting mold using 1.2343. The material’s predictable behavior helped us finish faster and under budget while keeping quality high. This matters most for budget-driven jobs where speed and efficiency decide success.
Cost
1.2343 is more cost-effective than 1.2344, mainly due to its lower alloy content. From my experience, this makes it an excellent option for projects that demand budget-conscious decisions. I’ve worked on several manufacturing jobs where cost was a major factor, and in those cases, 1.2343 came through perfectly. Its reduced alloy mix doesn’t sacrifice essential performance, making it a reliable steel choice when financial flexibility is limited. The practical advantages of 1.2343 lie in its balance—offering great toughness at a lower price point without compromising key features.
Applications
1.2343 and 1.2344 tool steels are dependable in tough conditions. They excel in high-pressure environments like die casting, forging, and plastic molding. These steels perform well under extreme heat, where precision and durability matter most. Both have their own advantages but are designed to succeed in the most demanding industrial tasks.
| Steel Grade | Applications |
|---|---|
| 1.2343 (H11) | Die casting tools for aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys Forging dies and inserts Extrusion tools for light metals Hot work punches and mandrels Plastic injection molds Ejector pins Tool holders and chucks |
| 1.2344 (H13) | Die casting dies for aluminum and magnesium at higher temperatures Forging dies for steel and titanium Extrusion tools for steel and high-temperature alloys Hot trimming tools Hot shear blades Pressure die casting tools |
Key Differences in Application
1.2344 is selected for more demanding high-temperature applications due to its superior hot hardness and wear resistance.
1.2343 is better suited for larger dies or tools with complex geometries, offering improved toughness.
1.2344 is favored for high production volumes and longer run times, particularly in severe service conditions.
Both steels are commonly used in similar industries, but 1.2344 is typically chosen for applications that require higher performance and tool longevity, often influenced by operational temperature, production scale, and cost factors.
Availability
Both grades are sold globally through major suppliers. From my experience, 1.2343 is easier to get immediately, while 1.2344 often needs advance planning for custom orders or rare sizes. I recommend ordering early if you need special treatments like heat processing or certifications – these add time to deliveries for both steels.
1.2343 (H11) Availability
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Stock Availability | More frequently stocked than 1.2344 |
| Price | Costs less than 1.2344 in most cases |
| Size Options | Round bars (8 – 400mm), plates (16 – 500mm), and slabs |
| Delivery Time | Standard sizes ship in 1 – 4 weeks |
| Monthly Supply | Major suppliers can deliver up to 2000 tons |
1.2344 (H13) Availability
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Stock Availability | Limited stock, requires more careful checking of supplier inventories |
| Price | Priced higher than 1.2343 |
| Delivery Time | Some sizes take 2 – 6 weeks to ship |
| Monthly Supply | Major suppliers offer up to 1000 tons |
summary
In the end, choosing between 1.2343 or 1.2344 tool steel depends on your project’s specific needs. Each has its advantages: 1.2343 offers toughness, while 1.2344 excels in heat resistance. Consider your application carefully to ensure the best performance and long-lasting tools. It’s all about making the right choice for the task.